$6B Boston Dynamics Buy
Hyundai Expands Korea’s Grand Robotics Plan

Hyundai to buy thousands of Boston Dynamics robots to advance manufacturing in the U.S. and Korea
Team Korea’s plan
Team Korea is at it again, this time stopping by its U.S. subsidiary Boston Dynamics to unfold more of its aggressive master plan for robotics superiority. Aside from China’s plan for robot-driven automation, Korea is the only other of the developed nations to have such a definitive plan.
See related: Major Growth Spurt Ahead for Korean Robotics
The Korean government enacted the Intelligent Robot Development and Distribution Promotion Act in 2008, establishing and pursuing policy measures for sustainable development of the robotics industry by promoting the development and promotion of robots, thereby developing the robotics industry as the nation’s key industry.
Every five years or so, Korea dedicates more investment monies into the plan. Due to the peculiarity of the robotics sector, i.e., broadly related industries both upstream and downstream, each government department is pushing for policy projects to foster and advance the robotics industry.
See related: Korea Gets Serious About Robotics
Korea, with the fourth largest economy in Asia—tenth worldwide—announced, in July of 2020, its National Strategy for a Great Transformation: The Korean New Deal. As then-President Moon commented: “The Korean New Deal will set the foundation for Korea’s next 100 years.”
Korea has been pushing the envelope ever since.
Now comes another ramp up in the plan. In a bold move to transform the future of manufacturing and robotics, Hyundai Motor Group has announced plans to deploy tens of thousands of robots from its subsidiary Boston Dynamics across its U.S. operations and at home in Korea
This strategic initiative signals Hyundai’s commitment to robotics innovation and positions it as a major player in global industrial robotics as well as in the exponential rise of humanoid robots.
Korea’s ambitious leap toward robot-driven manufacturing
The collaboration between Hyundai and Boston Dynamics is set to dramatically increase automation in Hyundai’s advanced manufacturing operations. Hyundai acquired Boston Dynamics from SoftBank in 2021 for $880 million, and since then has gradually integrated the company’s cutting-edge robotics into its production lines. Now, that integration is being scaled at an unprecedented level.
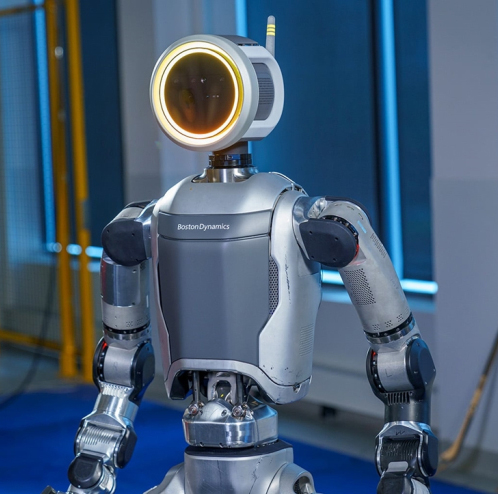
Hyundai confirmed that thousands of Boston Dynamics’ industrial robots, including the Atlas humanoid robot, which was recently upgraded to an electric version, is expected to play a significant role in assembly tasks, helping optimize logistics and improve workplace safety.
The investment is part of Hyundai’s recently announced $21 billion commitment to U.S. operations. This package includes $6 billion earmarked for expanding innovation, strategic partnerships, and next-gen technologies like AI and robotics.
Boston Dynamics’ role in Hyundai’s “Next Chapter”
Boston Dynamics, which originated from MIT’s Leg Lab and became widely known for its highly agile and expressive robots, is now evolving into a cornerstone of Hyundai’s smart mobility vision. At the recent all-hands meeting at Boston Dynamics’ headquarters in Waltham, Massachusetts, Hyundai Motor Group Chairman Chung Euisun and Vice Chairman Jaehoon Chang emphasized their shared vision for using “physical AI” to reshape industrial processes.
“Robotics AI is central to our transformation,” Chang said. “Our partnership with Boston Dynamics will speed up our ability to lead in this industry.”
Physical AI refers to the combination of robotics hardware with advanced AI models that can perceive, adapt, and learn in real-world environments—pushing the envelope beyond what’s achievable with static, rule-based systems.
Scaling up: Hyundai’s Metaplant America and beyond
Hyundai’s newly launched Metaplant America in Georgia is already showcasing the real-world applications of Spot. The robot is currently used to monitor weld shop inspections, detecting anomalies and minimizing safety risks. Once Atlas becomes commercially viable for industrial use, it will be deployed alongside Spot to perform tasks like part transportation and real-time quality checks.

Boston Dynamics is also collaborating with NVIDIA to integrate its AI compute platforms into Atlas, improving the robot’s object recognition, motion planning, and behavior prediction capabilities. At NVIDIA’s GTC 2024, Boston Dynamics demonstrated how its AI-powered systems will advance capabilities in manufacturing and logistics.
The broader ecosystem: Toyota, TRI, and other partnerships
This robotic revolution is not unfolding in isolation. Boston Dynamics is also collaborating with the Toyota Research Institute (TRI) to develop general-purpose humanoids. The joint effort merges TRI’s large behavior model learning with Atlas’ mechanical agility, paving the way for robots capable of performing a wide array of tasks—from handling car parts to supporting warehouse logistics.
According to TRI CEO Gill Pratt, “The opportunity to implement our AI models on Boston Dynamics’ hardware opens up new possibilities in human-assistive robotics.”
This initiative adds to a growing network of partnerships aimed at rapidly advancing humanoid capabilities. Boston Dynamics is also working with Google DeepMind, Waymo, and its sister organization, the Robotics & AI Institute (RAI), to explore scalable training methods and diverse robot applications.
Humanoid robots: the next frontier in industrial automation
Boston Dynamics’ newly released electric Atlas robot, unveiled in early 2024, demonstrates enhanced dexterity and strength. In a demonstration video released by Hyundai, the robot is seen navigating complex tasks such as transporting engine components, adapting to different shelf configurations, and correcting placement errors in real time.
By integrating facial recognition cameras and adaptable grippers, the new Atlas robot can assess the layout of its surroundings and perform tasks with near-human efficiency. Hyundai aims to launch test operations by the end of 2025, with robots working alongside human employees to handle repetitive tasks and reduce physical strain.

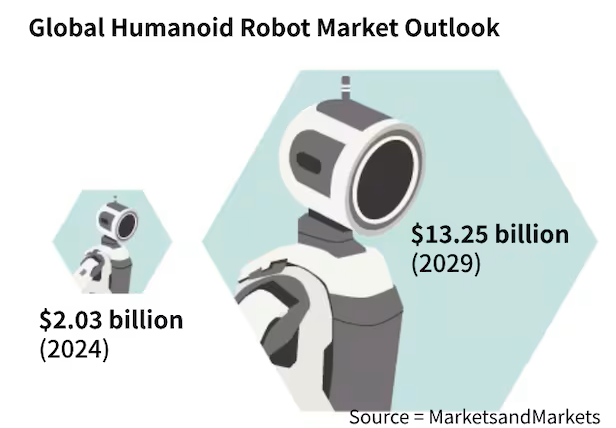
According to industry projections, the global humanoid robot market is expected to exceed $38 billion by 2035. Hyundai’s strategy positions it as a leader in this expanding field.
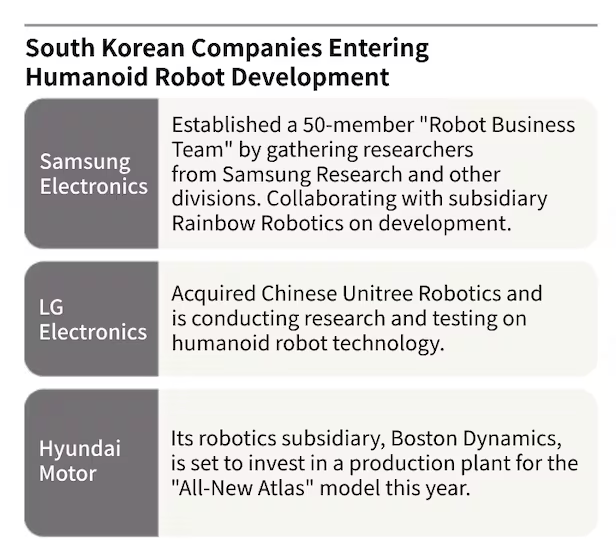
Competitive landscape: Korean giants enter the ring
Hyundai isn’t the only South Korean conglomerate eyeing the humanoid robotics boom. Samsung Electronics recently consolidated its robotics R&D efforts into a dedicated unit, and has partnered with Rainbow Robotics—creator of the HUBO robot. The company is also preparing to launch a consumer robot named Ballie.
Meanwhile, LG Electronics has invested in U.S.-based Bear Robotics and is expected to debut its assistant robot Q9 later this year. LG’s CTO division is also experimenting with humanoid systems developed in collaboration with Chinese robotics company Unitree.
These tech giants are embracing “physical AI” as a long-term strategy, aiming to integrate generative AI models with physical robotic systems that replicate human movement and cognition.
Competition from the West: Tesla, Meta, and Figure AI
U.S.-based competitors like Tesla and Figure AI are also ramping up development of humanoid robots. Tesla has deployed its Optimus robots at its own factories for basic automation tasks, while BMW is currently testing Figure 02 humanoids in its South Carolina production facilities.
As the arms race in robotics heats up, Hyundai and Boston Dynamics’ early-mover advantage may give them the edge in scaling real-world deployments.
Robotics as a core pillar of Hyundai’s future
Hyundai Motor Group has made it clear that robotics will be a foundational part of its business. Chairman Chung Euisun previously outlined a vision in which 20% of Hyundai’s revenue would come from robotics, compared to 50% from automobiles and 30% from urban air mobility (UAM).
The company has been exploring various cross-sector opportunities in automation, including hydrogen-powered vehicles, Level 4 autonomy (in partnership with Waymo), and AI-integrated vehicle systems.
A global vision with local roots
The large-scale deployment of Boston Dynamics robots will begin with Hyundai’s U.S. operations but is expected to expand globally. “This is not just about the U.S.—this is about creating the most advanced robotics ecosystem worldwide,” said Robert Playter, CEO of Boston Dynamics.
With key facilities in South Korea, the U.S., and beyond, the partnership aims to accelerate the commercialization of general-purpose humanoids and make robotic labor a standard part of industrial operations.
Future prospects and challenges
While the benefits of automation are clear—greater efficiency, improved safety, and lower operational costs—there are challenges ahead. Training AI to operate reliably in chaotic, unpredictable environments is still an evolving science. Integrating humanoids at scale will also require updates to safety protocols, labor training, and cross-system communications.
Nevertheless, Hyundai’s aggressive strategy indicates a deep belief that the rewards will outweigh the risks. With partners like Toyota, NVIDIA, and Google in its orbit, Boston Dynamics is poised to not just keep pace, but help set the standard for the robotics industry.


