
Putting Money on Robots
Picking Winners for Wall Street
Can a new age of robot tech spark new investments?
and robots are its epicenter!
Putting money on robots
Between its Factory of the Future event and the more recent research paper Investing in the Second Machine Age – Picking the Winners, Morgan Stanley (MS) has had an army of analysts scouring the globe for the best in technology while selecting out from among them “winners” worthy of investment.
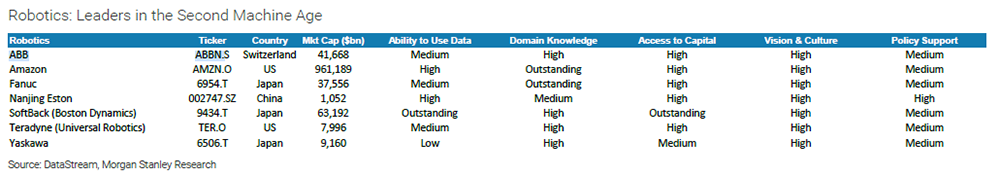
We took a look-see at what the MS army found, directing an even tighter eye at the seven publicly-traded robotics companies MS crowned as investment worthy:
ABB, Amazon, FANUC, Nanjing Estun, SoftBack (Boston Dynamics), Teradyne (Universal Robots), and Yaskawa:
High-tech winners
Overall, Investing in the Second Machine Age – Picking the Winners looked at these five broad technologies: Artificial Intelligence (AI), Industrial Software, Semiconductors, IoT Hardware, and Robotics as the technology power brokers of the near and far future.
All five were fascinatingly revealed by the MS teams! There’s amazing tech going on at breakneck speed; and it’s interesting to note how pervasive Robotics is across the entire tech set.

Subsequent columns here in Asian Robotics Review will cover all five tech categories individually, but this time around we’ll concentrate on Robotics, with a consideration to those investors on the prowl who are thinking about putting a few quid into robotics.
MS has picked out five of the seven, publicly-traded robotics manufacturers, for some investment scrutiny:
ABB, FANUC, Nanjing Estun, Teradyne (Universal Robots), and Yaskawa.
FANUC: Top Choice in Robotics FANUC (FANUY)
Why?
FANUC holds the top global market share in the industrial robot market. With its outstanding business model and strong competitiveness, high levels of growth look sustainable over the long term, and we think it is one of the best positioned companies among Factory Automation (FA) equipment/robot makers in particular and in the wider machinery and capital goods industry.
FANUC’s key competitive advantages:
- Internal production of core components for industrial robots such as NC systems and servo motors;
- Track record of many projects with automakers in various countries; and
- Progress in the development of non-automotive applications (we [MS] estimate sales to the auto industry account for about 50% of the company’s total robotics business). We [MS] expect these will support further expansion of its market share in industrial robots going forward.
Long-term drivers:
- With issues such as rising wages and labor shortages becoming more profound, users are having to invest in automation in order to reduce man-hours and enhance efficiency. The auto industry has been introducing industrial robots for some time, but we expect the scope of their use will expand, and we see growing needs for investment in automation using industrial robots across a broad range of fields.
- FANUC’s internal production of major components gives its industrial robotics business competitive and technological advantages, and we expect the business to remain a key driver propelling the company’s growth.
- The FIELD (FANUC Intelligent Edge Link and Drive) System developed by the company is an open platform that supports productivity and efficiency improvements at factories by collecting and analyzing data from sensors installed in various types of FANUC equipment, including robots.
- The system allows links to equipment made by other companies, and can also be used with third-party apps as well as FANUC’s own. As part of a strategy of capturing a large number of users, we expect earnings contributions from a long-term perspective.
How FANUC stacks up
Ability to Use Data – Medium: FANUC uses its open-platform FIELD System (Fanuc Intelligent Edge Link and Drive System) of sensors embedded in its products, including robots, to obtain data for analysis and use in supporting enhancements to factory productivity and efficiency. However, its progress in rolling this out in Business in practice has been a little slow.
Domain Knowledge – Outstanding: FANUC’s strong technological capability and competitiveness are the reason for its No.1 position in the global industrial robots market.
Access to Capital – High: FANUC is listed in Tokyo with good liquidity, and keeps a healthy level of cash.
Vision & Culture – High: FANUC is a market leader in CNCs, industrial robots and small machine tools. It is also working to extend its offerings from traditional products/services to open platforms like the FIELD System, utilizing IoT and AI.
Policy Support – Medium: The company benefits from government subsidies in the Chinese market, but receives no major policy support in other regions.
ABB is the global #2 in Robotics and Discrete Automation, with 2018 revenues of ~$3.6B, a 14.6% operating margin and a 5% market share. We have estimated unit sales of ~19k units per annum, based on value share (though this is not confirmed by the company).
ABB has a significant manufacturing base in Shanghai, and is the leading robotics supplier in China today. Automotive applications are c.45% Food & Beverage and 35% Pharma. We estimate the robotics operations are around 13% of the entire company.
We rate ABB’s Ability to Use Data as ‘Medium’ only, because it does not yet have a meaningful subscription-based software offering, or indeed a Top 3 PLC offering in factory hardware (6% share according to Statista); Domain Knowledge is rated ‘High’ because Process Industries (Oil & Gas, Chemical) is very strong, but penetration rates have been lower in other factory-based sectors; Access to Capital is ‘High’ ($44bn total assets) but annual R&D spend of ~4% of revenue compares with an 11% average for our Champions, ie. less than half; Vision & Culture is also rated ‘High’, because ABB is a multi-industry company and not focused just on robotics; we rate Policy Support for robot vendors overall as ‘Medium’, with supportive policy in some countries (e.g. China) but also barriers elsewhere.
We see ABB as well positioned in principle, but it has not been as early as certain peers to build out a meaningful software and digital platform.
Nanjing Estun is a key domestic industrial robotic supplier in China, generating Rmb1.461B revenue and 8.0% EBIT margin in 2018. The company’s strategy is to grow its market by developing customized robotics & solutions for various industries, and avoid competing against global leading players in the automotive and consumer electronics industries, where competition is more intense.
We rate Estun ‘High’ in its Ability to Use Data, because the usage data from clients are critically important for Estun to improve its technology know-how. We rate Access to Capital as ‘High’, because it is widely viewed in the capital markets as offering long-term growth potential; we also rate Vision & Culture ‘High’ due to management’s strong strategic understanding on robotics, and we rate Policy Support ‘High’, based on the push by China’s government to advance the country’s manufacturing industry. We rate Domain Knowledge ‘Medium’, as Estun is a young industrial robotics company and is still expanding its domain knowledge to develop customized robotic products.
Universal Robots, global leader in collaborative robots. While Teradyne is a ~$2.1B diverse supplier of automation and test equipment, the company’s Universal Robots division is a leader in the small but quickly growing cobotics markets.
The lower price point and expanded applications by operating in “cageless” environments drove 38% growth in UR in 2018 up to US$234m in revenue. We estimate that UR’s collaborative robots business is larger than most of the other cobot franchises combined. We believe the expanded application set will allow Teradyne through Universal Robots to continue to drive strong growth beyond cyclical trends in traditional robotics sectors like automotive and electronics.
Teradyne’s broad hardware and measurement portfolio generates substantial data that is ultimately used by other automation nodes than in its own products, making it a ‘Medium’ on this criteria. In our other categories, Teradyne’s corporate scale, product leadership in its field, and dominant market share driving the highest installed base in a small but growing area of importance warrant a ‘High’ rating, in our view.
Yaskawa, one of the top robotics makers globally, with robotics revenue of ¥178bn and operating profit margins of 9.7% for F2/19.
The robotics business contributes around 40% of total revenue. Looking at the robotics revenue by end market, 50-60% comes from the automotive industry, while the remainder comes from general industries such as electronics, appliances and food/pharma.
The company has two main plants, in Japan and China. Production capacity has expanded to 4,000 units per month, with China production accounting for around 30% of the total.
We rate Yaskawa’s Ability to Use Data as ‘Low’, because it does not have a software offering. Domain Knowledge / Vision & Culture are rated ‘High’ in our matrix, given the company’s long history and extensive experience in the robotics market, as well as its new mid-term vision to expand its automation business through internal sales synergies and collaboration with other automation makers. We rate Access to Capital as ‘Medium’ because the company has less cash than with other FA names in Japan, and Policy Support as ‘Medium’ reflecting the stimulus policy in China but limited support in other regions.
